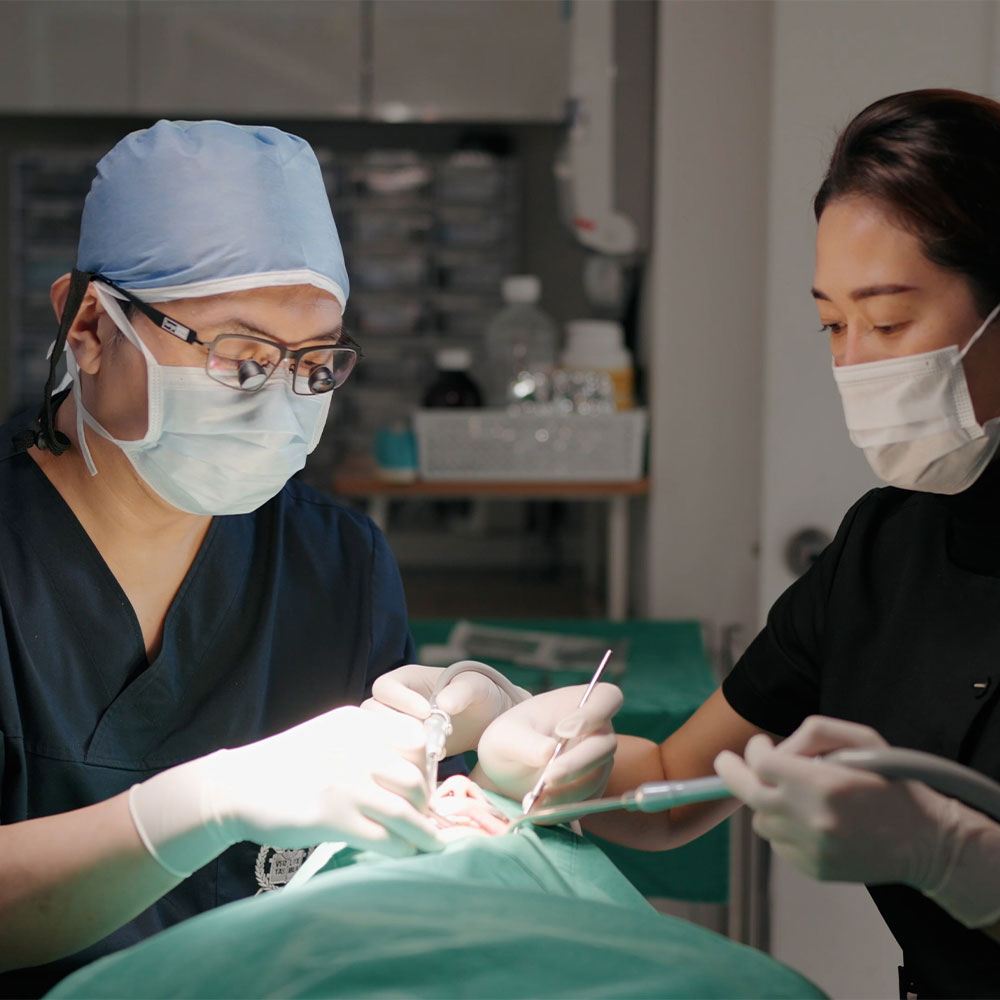
General bone grafting increases implant success rates
Reinforces insufficient jawbone to enable stable implant placement
What is General Bone Grafting?
A treatment that reinforces insufficient jawbone height or width using artificial bone or autogenous bone for implant placement. Graft material is placed in areas with insufficient bone to induce new bone tissue formation.
Immediate placement and bone grafting after extraction
Bone resorption process after extraction
After tooth loss, the jawbone gradually resorbs over time, making implant placement difficult
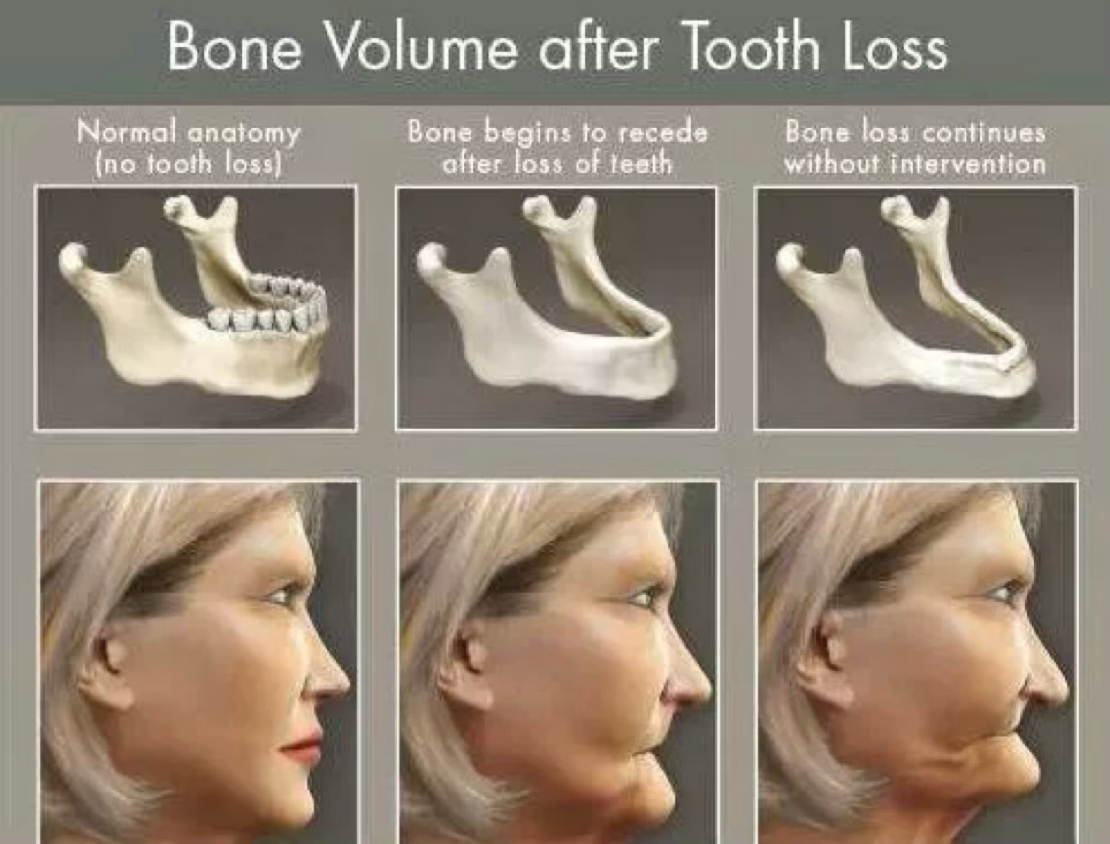
3 stages of jawbone changes after tooth loss
Normal anatomical structure
Healthy jawbone when tooth is present
Bone resorption begins
Rapid resorption 3-6 months after extraction
Continuous bone loss
Continues to worsen if left untreated
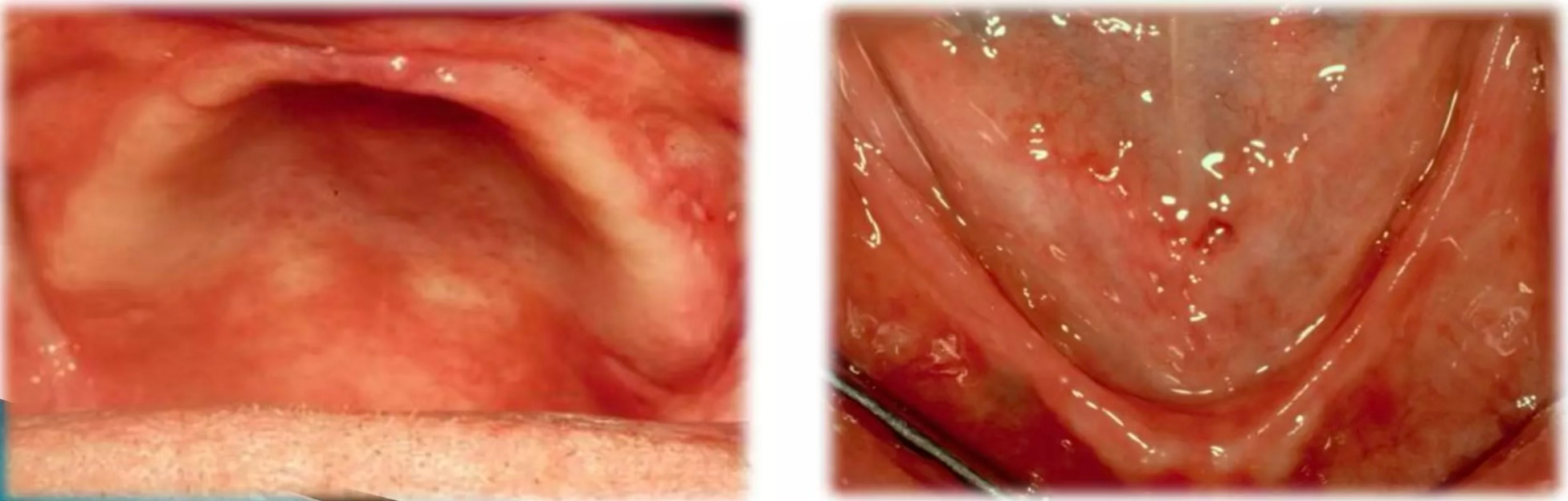
Bone resorption due to long-term denture use
Patients who have worn dentures for a long time experience severe jawbone thinning, requiring extensive bone grafting for implant placement.
⚠️ 50-70% bone resorption occurs with denture use over 10 years
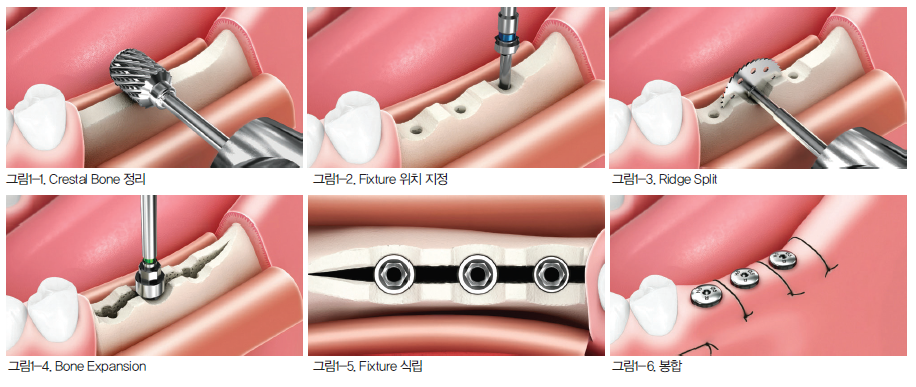
Width expansion surgery (Ridge Splitting)
A surgical method that separates the thinned jawbone and places bone graft material between them to increase width.
✓ Can expand from minimum 2-3mm width to 6-8mm
Cases requiring bone grafting
Sufficient bone volume and quality are necessary for implant success
Cases requiring immediate implant after extraction
Places implant immediately after tooth extraction to shorten treatment time and prevent bone resorption

Tooth damage due to trauma
When tooth is severely damaged by accident or impact, making extraction inevitable

Severe decay beyond preservation
When most of the tooth is decayed and difficult to preserve even with root canal treatment

Tooth mobility due to periodontal disease
When gum disease has progressed severely causing tooth mobility
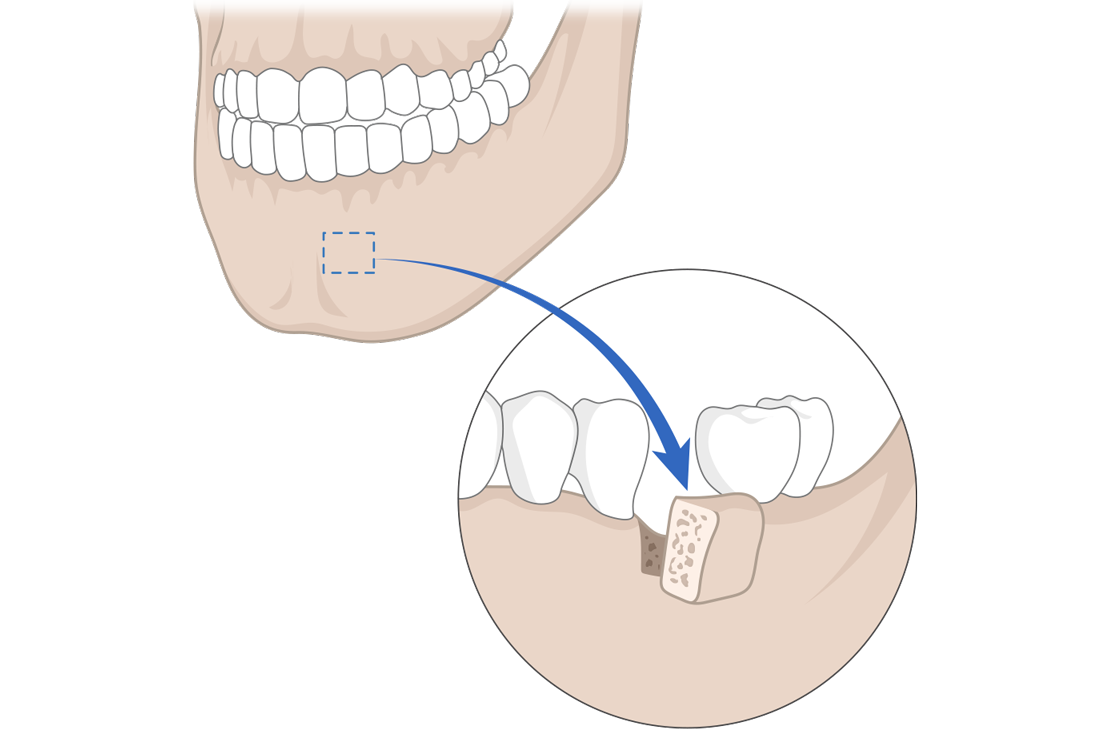
Why bone grafting is essential for immediate placement after extraction
The 1-2mm or larger gap between the extraction socket and implant must be filled with bone graft
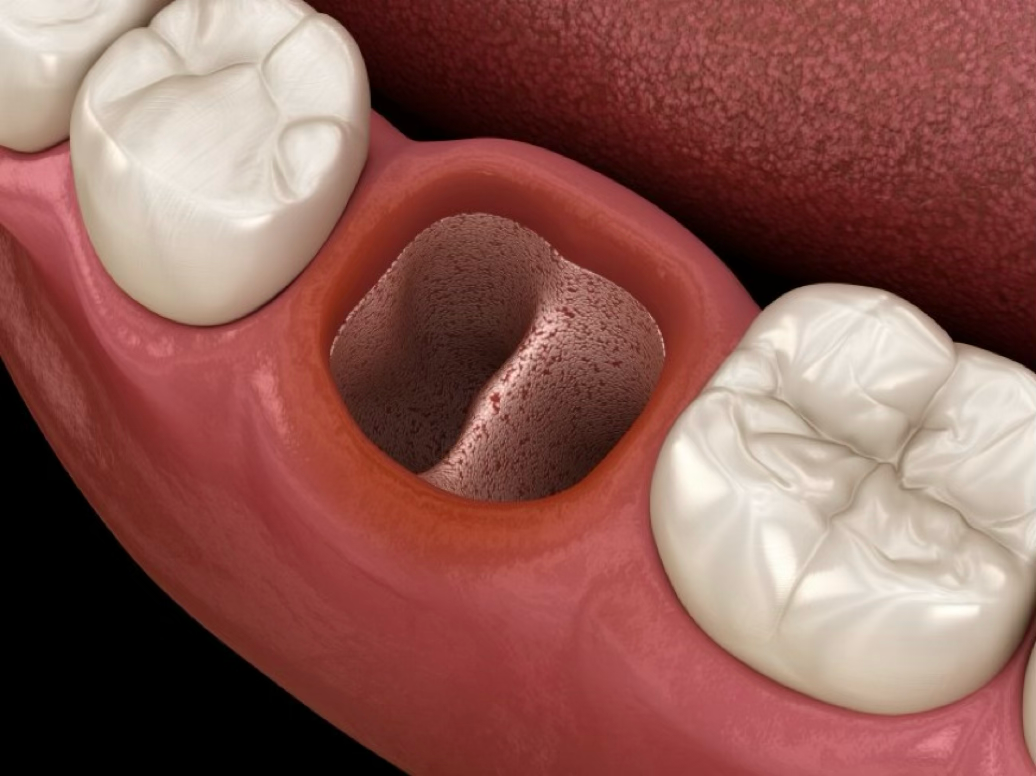
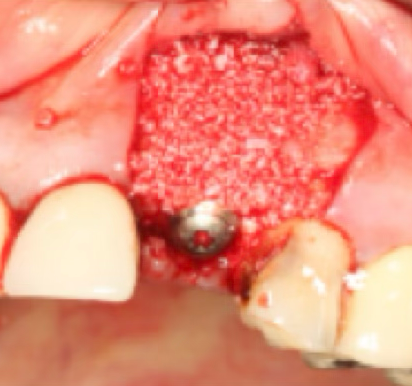
Stage 1: Socket after extraction
Empty extraction socket after tooth removal
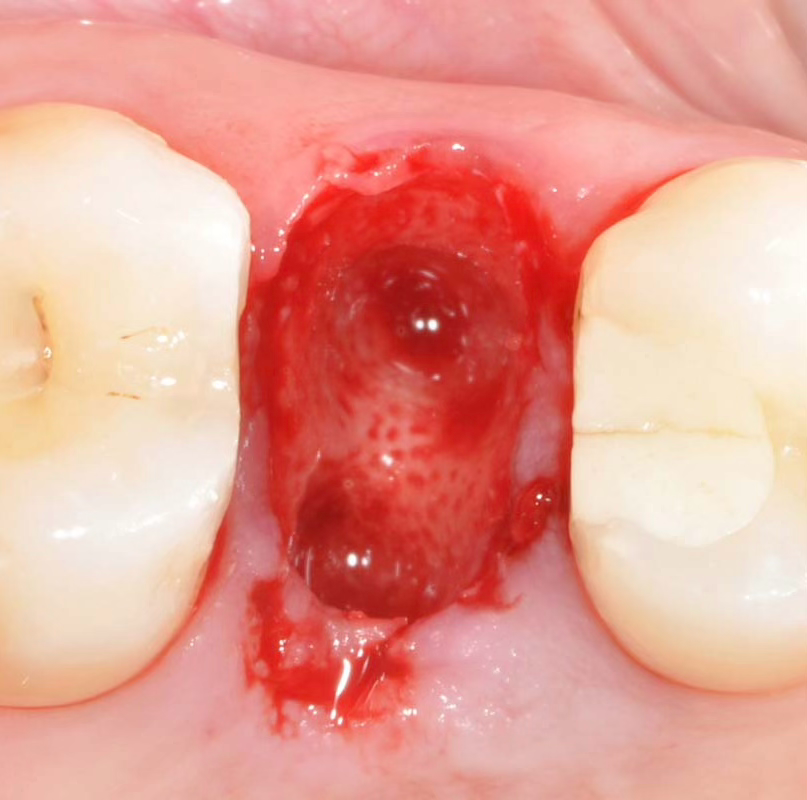
Stage 2: Actual extraction site
Actual clinical view showing wide empty space after extraction
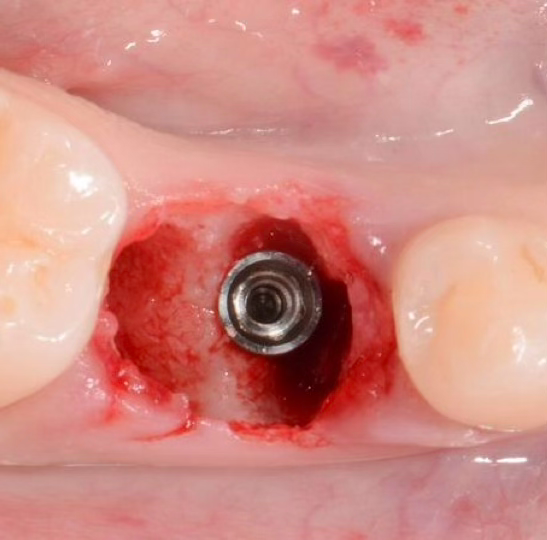
Stage 3: Implant placement
Gap between implant and extraction socket
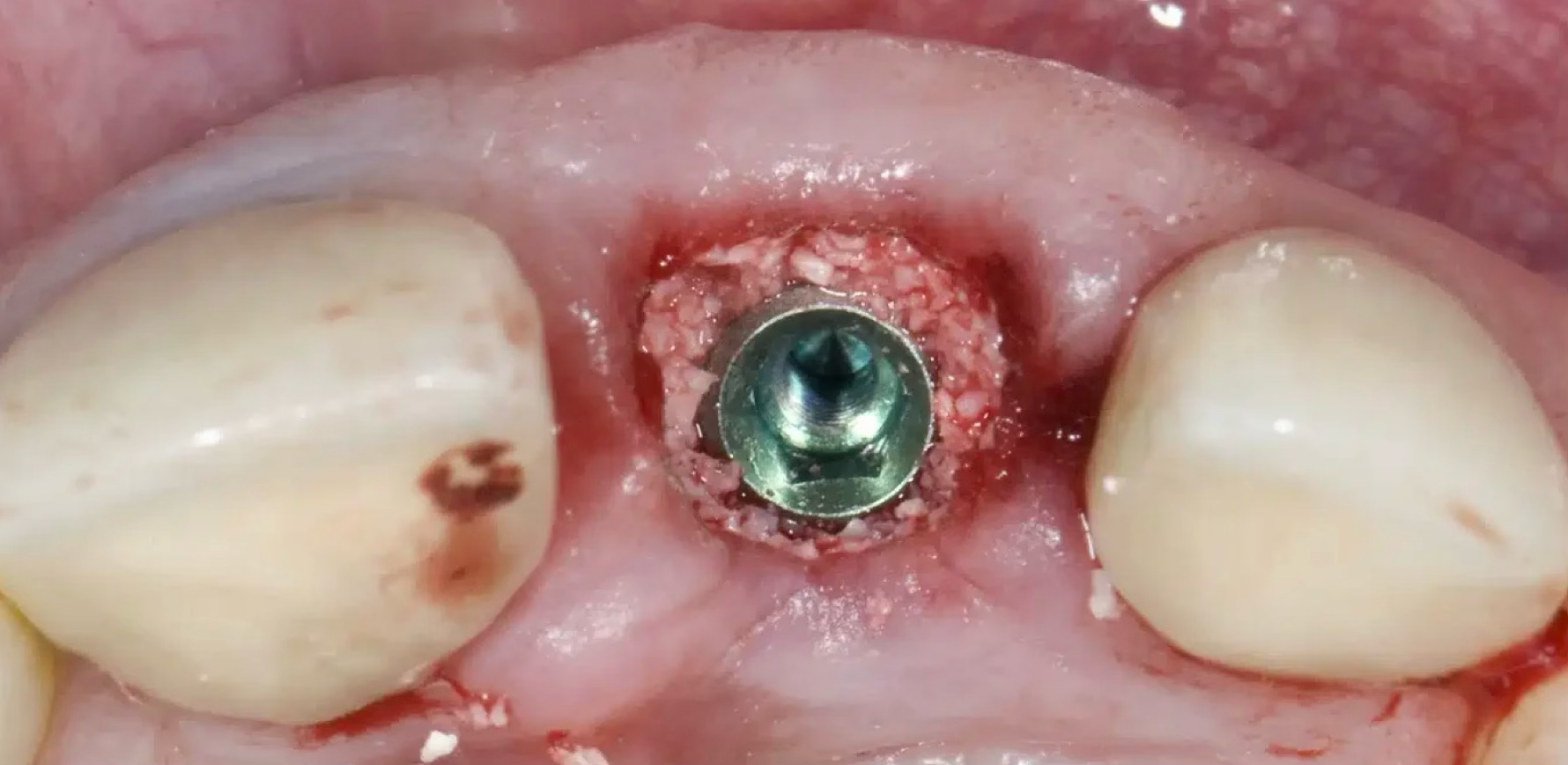
Stage 4: Bone grafting completed
Empty space perfectly filled with bone graft material
Important: Gaps of 1-2mm or more require bone grafting
- ✓Empty space between extraction socket and implant is difficult to heal naturally
- ✓Bone grafting improves stable osseointegration and implant success rate
- ✓Appropriate bone grafting ensures long-term stability
Insufficient bone width
When jawbone width is 2mm or less, making implant placement difficult
Minimum 6-8mm bone width required
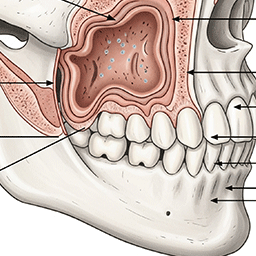
Insufficient bone height
When distance to maxillary sinus or inferior alveolar nerve is insufficient
Minimum 8-10mm bone height required

Bone resorption after extraction
When 40-60% bone resorption occurs 3-6 months after extraction
1-3mm vertical and 3-5mm horizontal resorption

Poor bone density
When initial fixation is difficult due to soft D3, D4 type bone
Bone grafting needed to improve bone density
Types of bone graft materials
Optimal graft material selected according to patient condition and needs
Autograft
Method using patient's own harvested bone, the most ideal graft material.
Main advantages
- Best biocompatibility
- Excellent bone formation ability
- Low infection risk
- No immune rejection
Allograft
Method using specially processed donated human bone.
Main advantages
- No harvesting surgery required
- Sufficient quantity available
- Safety ensured through processing
- Excellent osteoconductive ability
Xenograft
Method using purified animal bone, most widely used.
Main advantages
- Unlimited supply available
- Economical cost
- Excellent osteoconductive ability
- Stable quality
Synthetic
Artificially manufactured bone graft material, with Bio-Oss being representative.

Main advantages
- No infection risk at all
- Consistent quality guarantee
- Unlimited supply
- Uses biodegradable materials
Bone grafting surgical methods
Optimal surgical method selected according to patient condition
Width expansion surgery (GBR)
Surgery that uses bone graft material and barrier membrane to increase bone width when bone width is insufficient.
- Desirable bone regeneration using barrier membrane
- Prevents bone graft material displacement
- Implant placement possible after 3-6 months
- Predictable bone regeneration results
Height increase surgery
Surgery that vertically increases bone when bone height is insufficient.
- Sinus lift or inferior alveolar nerve repositioning
- Additional bone volume secured with block bone grafting
- Safe results through staged bone regeneration
- Minimum 6-month healing period required
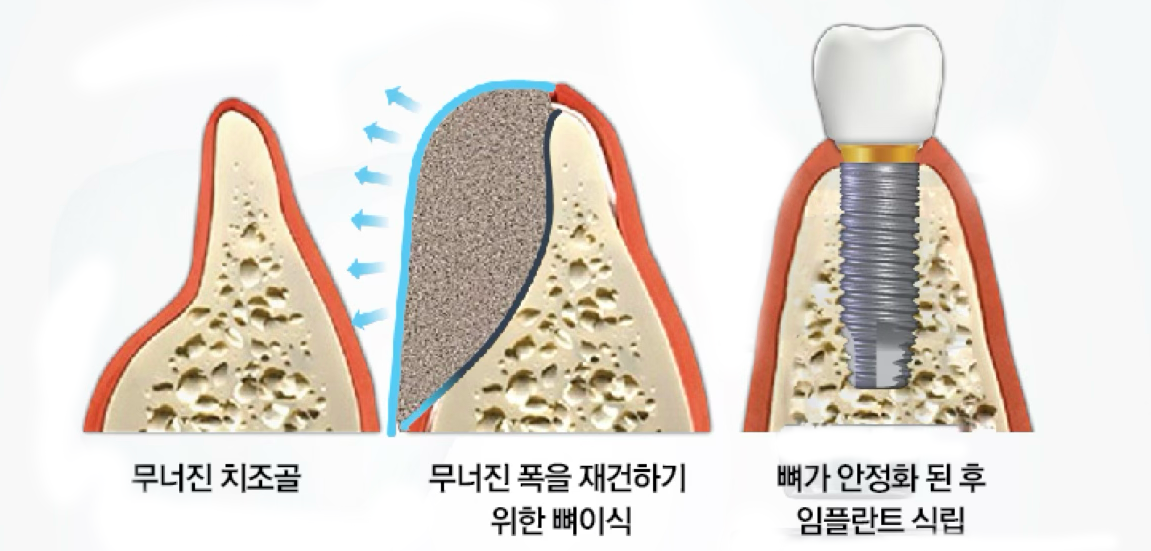
Horizontal bone augmentation (GBR)
Surgery using barrier membrane and bone graft material to horizontally increase bone width.
- ✓Space maintenance with barrier membrane
- ✓Implant placement after 4-6 months
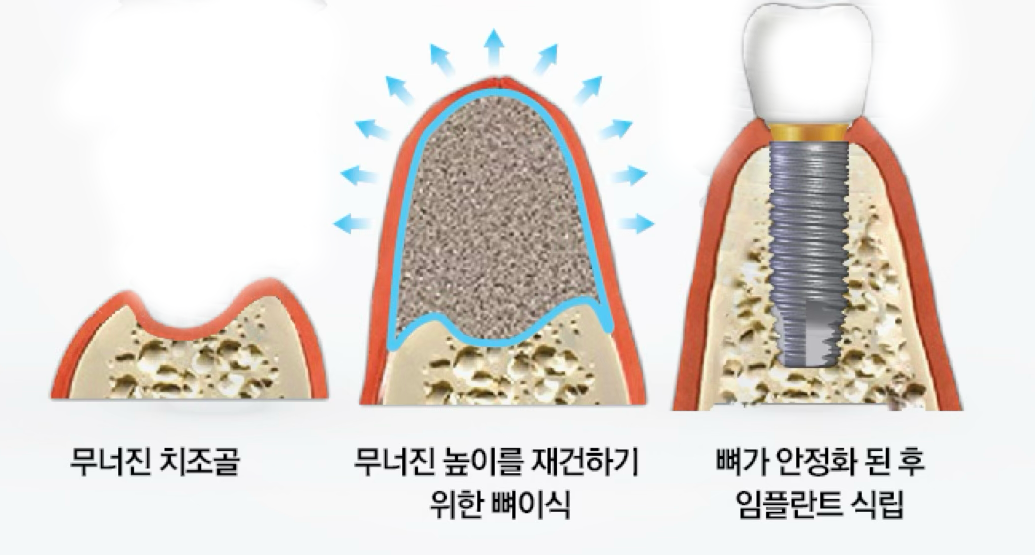
Combined horizontal/vertical augmentation
Complex surgical method that simultaneously increases width and height.
- ✓Resolves severe bone defects
- ✓Three-dimensional bone regeneration
Cases requiring block bone grafting
Cases where block-type autogenous bone grafting is needed due to extensive bone defects.
Full arch implant
When all teeth are lost
Sinus lift surgery
For extensive bone grafting
Traumatic bone defect
Bone defect due to accident
Congenital defect
Defect present from birth
Advantages of block bone grafting
- ✓Secures large bone volume
- ✓No rejection with autogenous bone
- ✓Predictable results
- ✓Prevents thermal damage
Bone regeneration using titanium mesh
State-of-the-art surgical method for resolving extensive bone defects
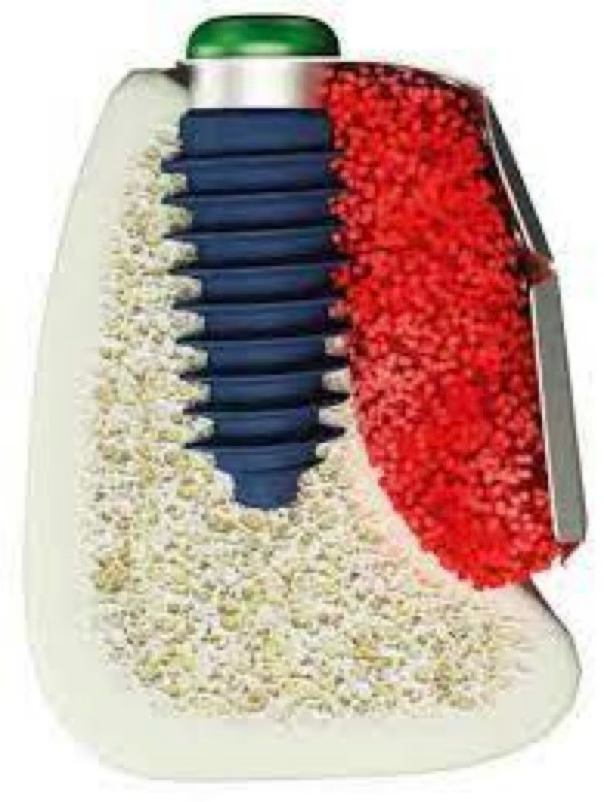
Titanium mesh 3D diagram
Creates patient-customized titanium mesh to regenerate bone in precise form.
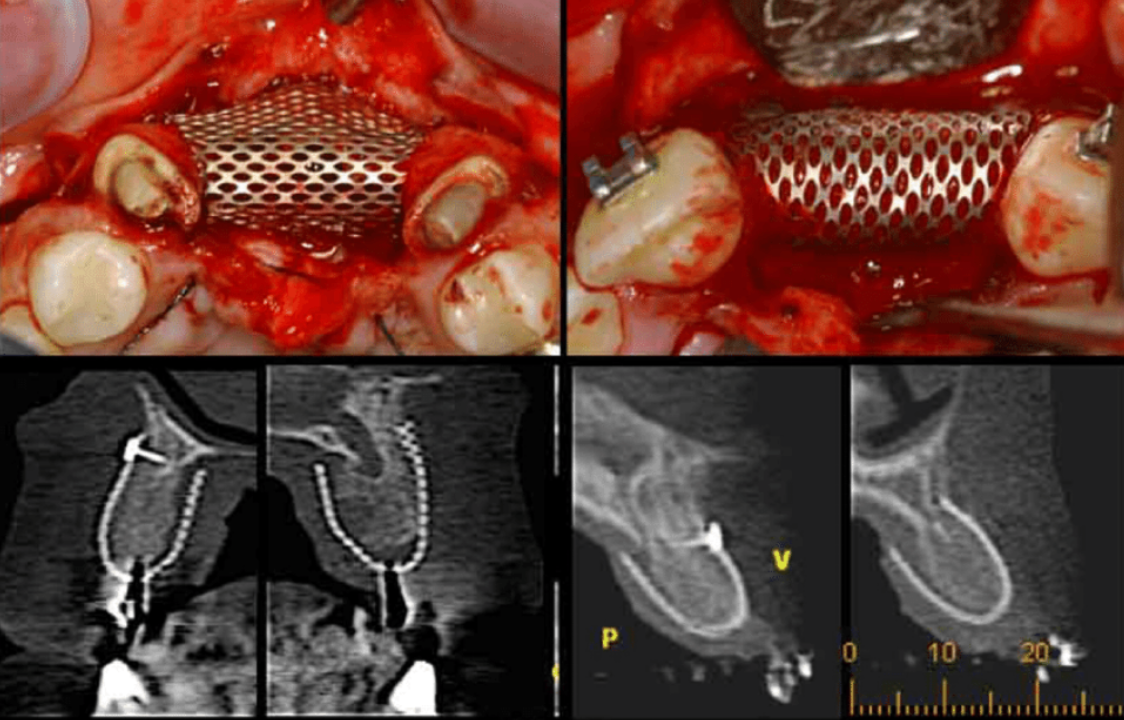
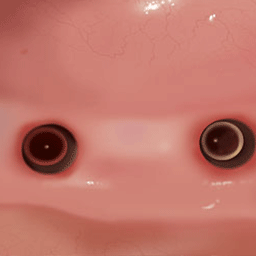
Mesh surgery clinical photos
Actual clinical case with titanium mesh application
Bone grafting success case
Successfully regenerated bone after mesh removal
Precise shape maintenance
Achieves desired form with 3D custom fabrication
Stable space securing
Blocks soft tissue infiltration and protects bone regeneration space
Extensive bone regeneration
Effective even for severe bone defects
High success rate
Over 95% clinical success rate
Treatment process
Systematic treatment process for safe and accurate surgery
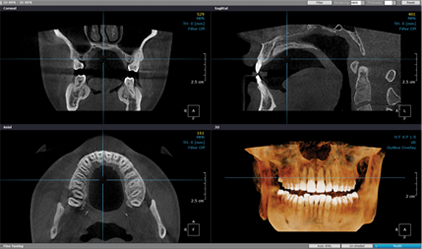
Diagnosis and treatment planning
Thoroughly diagnose condition using panoramic, X-ray, 3D CT, then establish treatment plan.
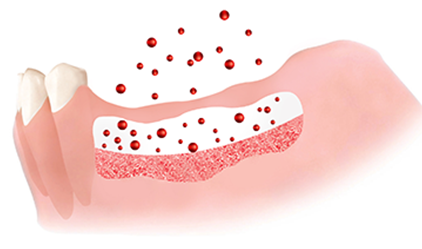
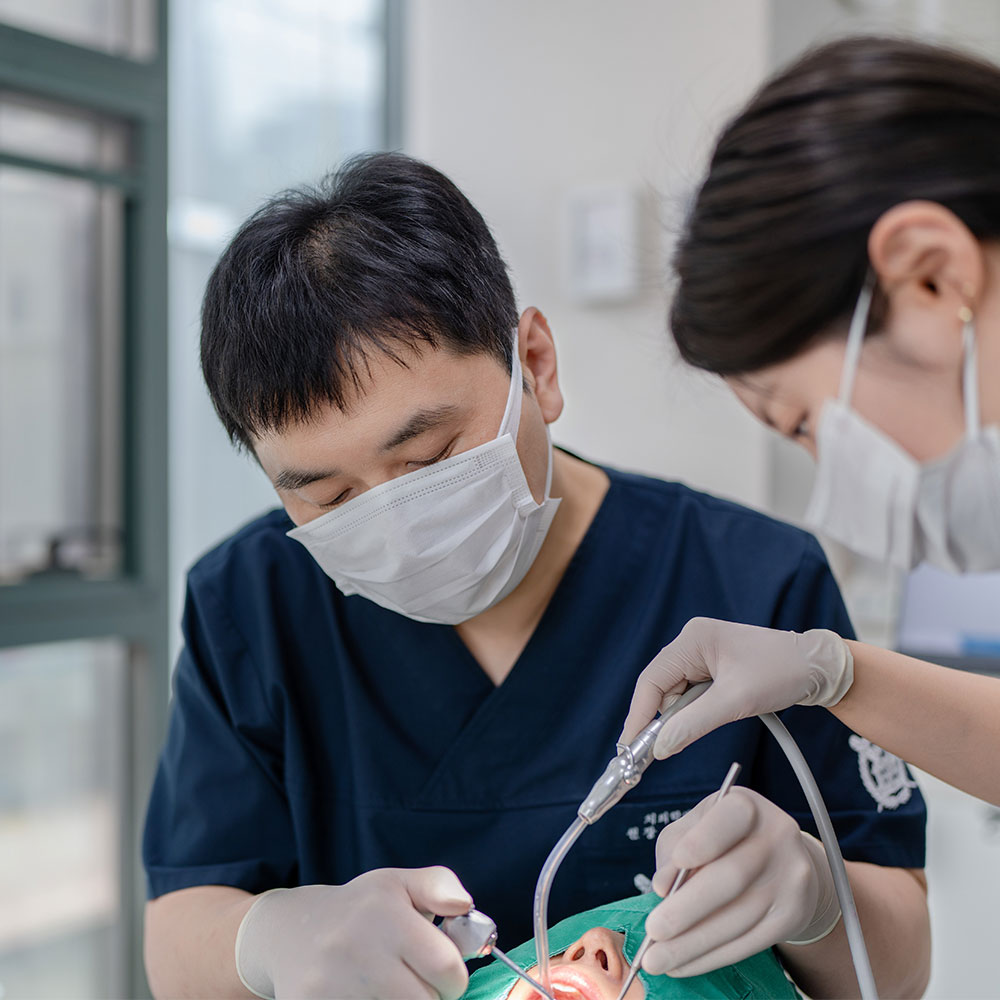
Jawbone grafting
After cleanly removing inflammatory tissue from bone destruction area, apply bone graft material and cover with biomembrane to protect graft site.
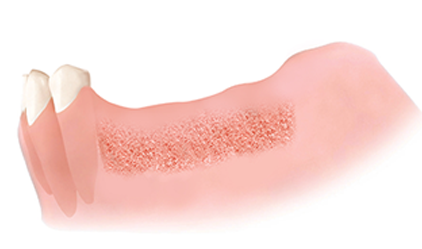
Surgical site suturing
Manipulate flap to prevent gum separation, then suture.
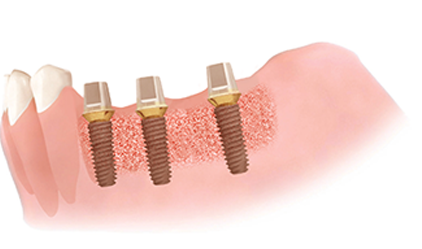
Implant placement
Place implant once jawbone has formed.
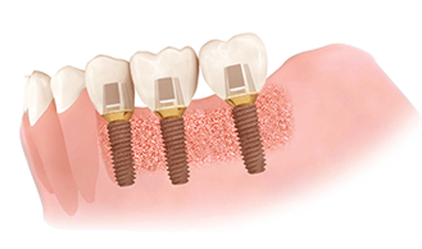
Prosthetic connection
Connect prosthetic to reproduce natural tooth appearance and function.
ATTENTION
W DENTAL CLINIC SURGERY
Please check precautions before/after surgery.
Bone graft implant precautions
If the gum opens, the amount of regenerated bone significantly decreases.
Guided bone regeneration stretches and sutures the insufficient gum as much as the reinforced bone, making it prone to opening. Therefore, much care is needed to prevent stimulation to the surgical site.
Avoid smoking, drinking, hard or chewy foods and take prescribed medications well.
Avoid brushing near the surgical site and rinse with prescribed antiseptic.
Avoid strenuous exercise or overwork as they can interfere with healing.
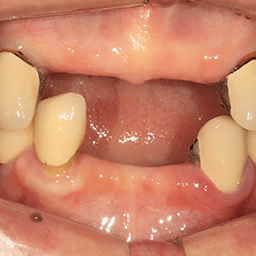
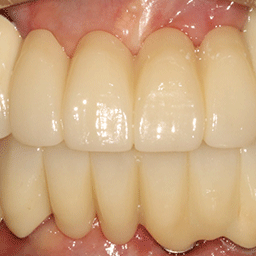
W Dental Clinic Before & After
Before and after treatment photos
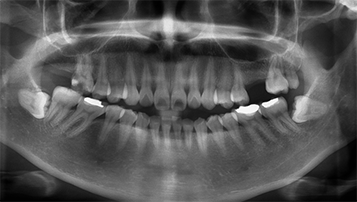
Before
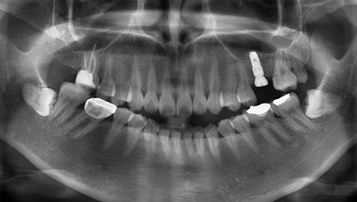
After
Bone grafting

Get bone grafting consultation
Receive consultation for personalized bone grafting treatment plan
Experience safe and clean treatment with our 12-step perfect sterilization system
☎ 1660-0752